Click HERE to see the CDC recommendation for RSV vaccination for adults
You are about to leave a GSK website
You are about to leave a GSK website. By clicking this link, you will be taken to a website that is independent from GSK. The site you are linking to is not controlled or endorsed by GSK and GSK is not responsible for its content.
YOUR ADULT PATIENTS’ PROGRESS MAY BE CUT SHORT BY RSV1
Older adult patients, including those with certain comorbidities, are at an increased risk of severe RSV1
RSV is a common and contagious respiratory virus that can cause lower respiratory tract disease (LRTD), including complications such as pneumonia and exacerbations of COPD, asthma, and CHF.1
Severe RSV can lead to hospitalization and even death2


Recognize the threat of severe RSV for older adult patients
In a study conducted between January 2011 and June 2015 among patients aged 60 years or older hospitalized with RSV (N=645)3*:
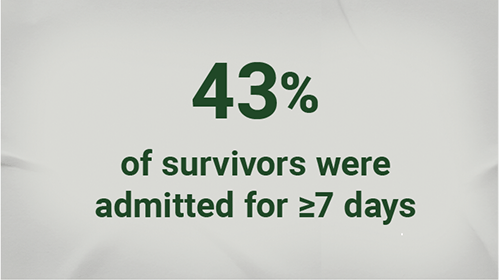
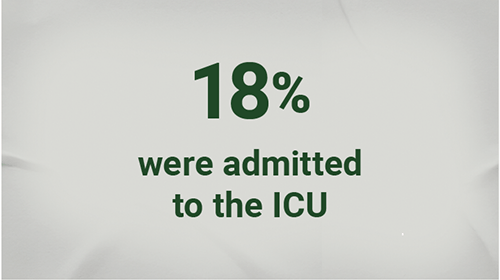
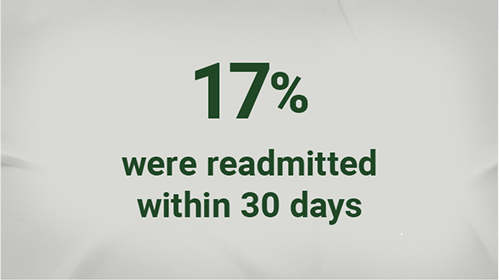
- *
An observational, retrospective, cohort study conducted at an integrated health system evaluated adults aged ≥60 years hospitalized with RSV infection (n=645) or influenza infection (n=1878) over 5 consecutive seasons between January 2011 and June 2015 to compare demographics, prehospitalization characteristics, hospital utilization, and clinical outcomes.
See how severe RSV can impact patients
Patients aged 60 years and older who were hospitalized with RSV experienced serious clinical outcomes3
Rates of events during hospitalization among adults aged 60 years or older with RSV3†:
37.7%
Cardiovascular complications‡
18.9%
Acute renal failure
16.9%
Respiratory exacerbations§
- †
An observational, retrospective, cohort study conducted at an integrated healthcare system evaluated adults aged ≥60 years hospitalized with RSV infection (n=645) or influenza A/B infection (n=1878) over 5 consecutive seasons between January 2011 and June 2015 to compare demographics, prehospitalization characteristics, hospital utilization, and clinical outcomes. Patients with RSV had the following rates of comorbidities 1 year prior to admission: 32.2% had ischemic heart disease; 35.3% had CHF; 38.9% had diabetes; 29.8% had COPD, chronic bronchitis, or emphysema; 26.0% had asthma; and 5.6% had end-stage renal disease.
- ‡
Defined as myocardial infarction, pericarditis, endocarditis, myocarditis, or atrial fibrillation.
- §
Defined as exacerbation of COPD, chronic bronchitis, or emphysema.
Talk to your adult patients about the threat of severe RSV

See Irene’s journey with RSV
Hear Irene tell her own story of RSV.
CHF=chronic heart failure; COPD=chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ICU=intensive care unit; RSV=respiratory syncytial virus.
References
Respiratory syncytial virus infection (RSV). RSV in adults. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed July 9, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/adults/
Falsey AR, Hennessey PA, Formica MA, Cox C, Walsh EE. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(17):1749-1759. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043951
Ackerson B, Tseng HF, Sy LS, et al. Severe morbidity and mortality associated with respiratory syncytial virus versus influenza infection in hospitalized older adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69(2):197-203. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy991
